Tiny Houses Designs: United States vs. New Zealand
Scroll through Instagram and Facebook, and you’ll find beautiful tiny house designs from around the world. You may come across one from another country that catches your eye and that you want to build. Doesn’t seem too hard to take a design from another country and build it in the US does it? It might seem straightforward, but regulations and materials vary widely between countries. In this article, we’ll contrast New Zealand’s tiny house designs with those in the United States.
Size, Weight, and Measurement Regulations:
Width
Tiny houses in New Zealand must not exceed a width of 2.55m (8ft 4in) to be classified as road-legal. This width allows tiny houses to travel roads and highways safely without disruptions or special permits. In The U.S. the standard width allowed without permits is 8ft 6in or 2.59m. In the US, tiny houses are often 10ft wide, the most popular width. Acquiring a permit for this size typically costs between $14-35. Check this article for more information: Should you build a 10ft wide tiny house?

Height
The maximum height allowed in New Zealand is 4.3m (or 14ft 7in). New Zealand’s height regulations ensure tiny houses safely navigate under bridges and overpasses. Meanwhile, in the US, the standard height limit is 13ft 6in across all states. However, many West Coast states may permit up to 14ft, depending on the driver’s discretion. Even at 14ft, New Zealand still allows an extra 7in! Most US tiny house builders stick to a height of 13ft 6in. This means the average NZ Tiny House, like the Hazel from Shayes Tiny Homes, stands 1ft 1in taller. With a length of 30′ 2″, the width of 9′ 10″, and a 14′ 7″ height, the Hazel’s dimensions are undeniably appealing.
However, fitting it to US standards means making notable height changes inside. A client inspired by New Zealand designs came to us. We crafted a roomy design for her, but our height limits led to loft compromises. Watch the video ’28 x 10ft Tiny House Build In Progress’ to see the build’s progression.

Length
In New Zealand, there’s no set nationwide maximum length, but the Queenstown Government’s factsheet recommends not exceeding 39.4′. However, from practical experience, it’s advisable not to exceed 8.5m (27.9 feet) to maintain the weight limit. Length plays a pivotal role in a tiny house’s road maneuverability, particularly during turns or in tight spaces. In the vast expanse of the United States, the total length, counting the tow vehicle, can be up to 65ft. We offer bumper pull trailers up to 45ft and gooseneck trailers reaching 50ft.

Weight
The weight limit, including the trailer, is 3500kgs (7,716 pounds) in New Zealand. This weight limit ensures that standard vehicles can tow the tiny house without requiring specialized heavy-duty vehicles. In the United States, tiny houses often weigh more than 7,716 lbs, making that weight considered light. In the US, the average tiny house weight ranges from 14,000-18,000lbs, almost twice the towing capacity in New Zealand. For perspective, an 18ft x 8ft finished tiny house in the US typically weighs around 7,500lbs. However, by the 2020s, many deemed this size insufficient. By 2023, the typical tiny house measures 30′ – 36′ in length and 10′ in width, weighing an average of 16,000lbs upon completion.

Trailers
In New Zealand, trailers, including their own weight, have a limit of 7,716 lbs. Contrastingly, in the US, we craft custom tiny house trailers capable of supporting up to 28,000 lbs, including their own weight. This means our US tiny houses can be up to 3.63 times heftier than those in New Zealand. While 28ft is a common length in NZ, the US norm ranges from 30ft to 36ft. We’ve touched on these points before, so let’s delve into the significant trailer differences, focusing on Deck Heights and Fenders.

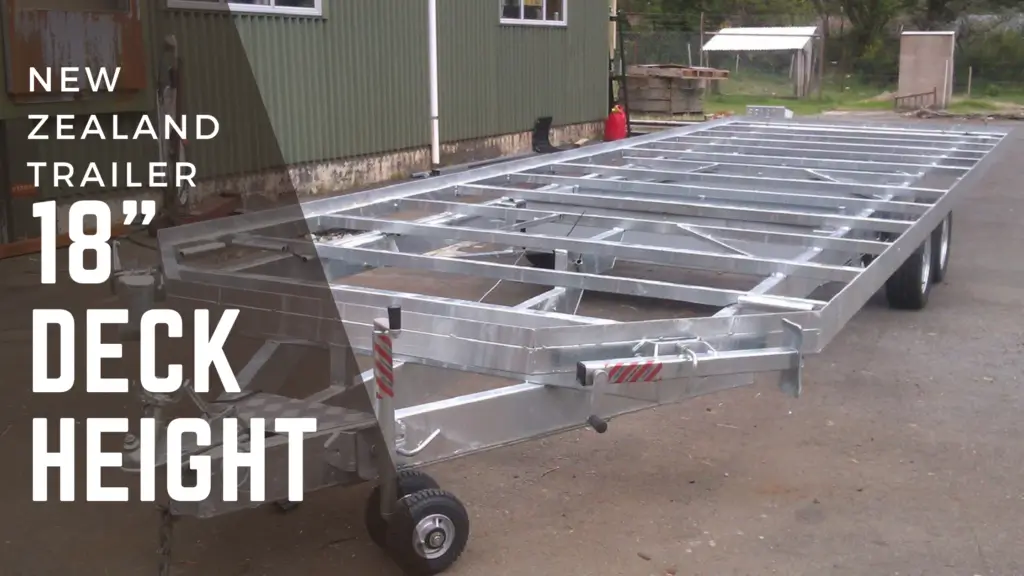
Trailer Deck Heights
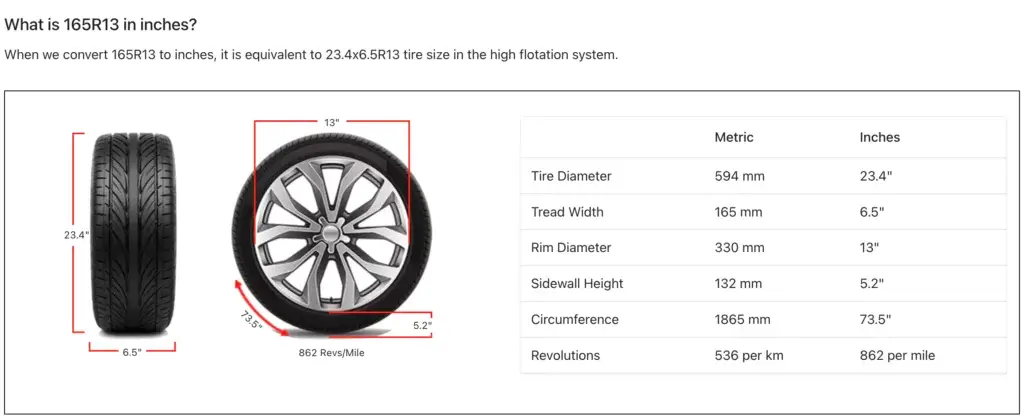
In New Zealand, given the trailer weight limit of 7,716lbs, it results in smaller load-rated tires, reduced frame sizes, and consequently, a lower deck height. they use 13” wheels (165R13C) on galvanized rims
In the US the standard wheel size we use is 16in Steel rims with 235/80/r16 tires

By opting for lower-profile tires, New Zealand gains an extra 7.5in in height, unlike the U.S., where we need larger tires to support our heavier tiny houses.
Deckovers
Using lower profile tires, builders often choose the Deckover trailer as the most common deck style. This style trailer has no fenders and is flat and completely covers the wheels. Consider a New Zealand Tiny House Trailer: its deck height measures just 18in from the ground to the deck’s top.
From Different Worlds
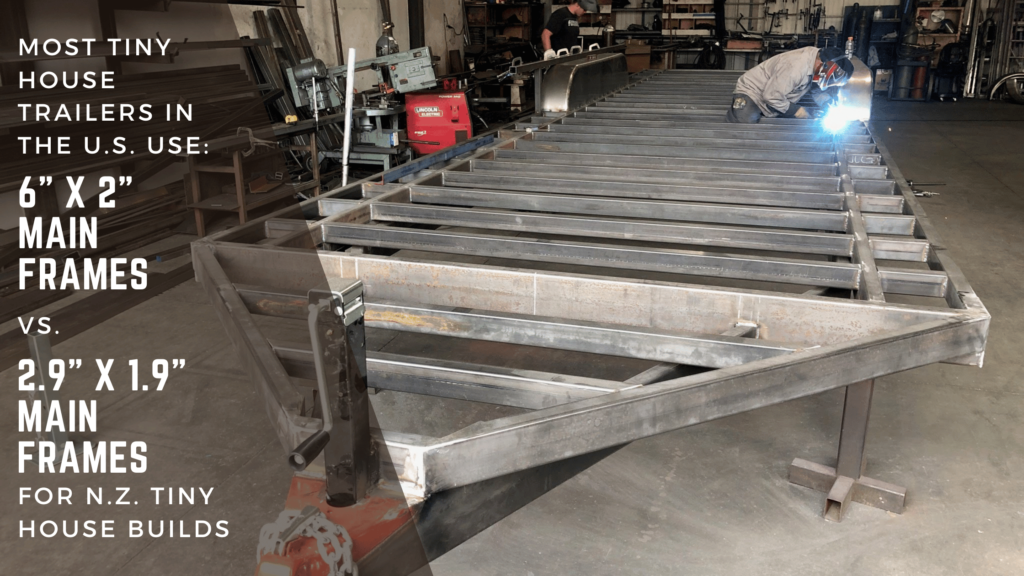
At this point, you still might be thinking, why is there still such a big height difference? The tires yes are 7.5in difference in height but what else is affecting the huge difference? The difference lies in the steel framing size of US versus NZ Tiny House Trailers. In New Zealand, the main frame measures 2.9in tall by 1.9in wide. In contrast, a US tiny house trailer typically has a frame that’s 6in tall and 2in wide. The pictured black trailer is a 30ft x 10ft wide 21k Deckover. It features a mainframe of 10in I beams with mounted axles and a 6×2 box tube frame deck for building. With 4×2 box tube crossmembers spaced 16in on center, these crossmembers stand over 1in taller than the mainframes found on a New Zealand tiny house trailer.
The crossmembers on a NZ trailer are only 2.5” tall x 1.3in wide. In the US to achieve a lower deck height, the best option is to have exposed fenders that you will need to build around but allow you to get as close to NZ deck heights as possible. If you order your Tiny House Trailer with 4″ drop axles, you can get a 22″ deck height (only 4in taller than a New Zealand trailer) and you will end up with fenders like these:
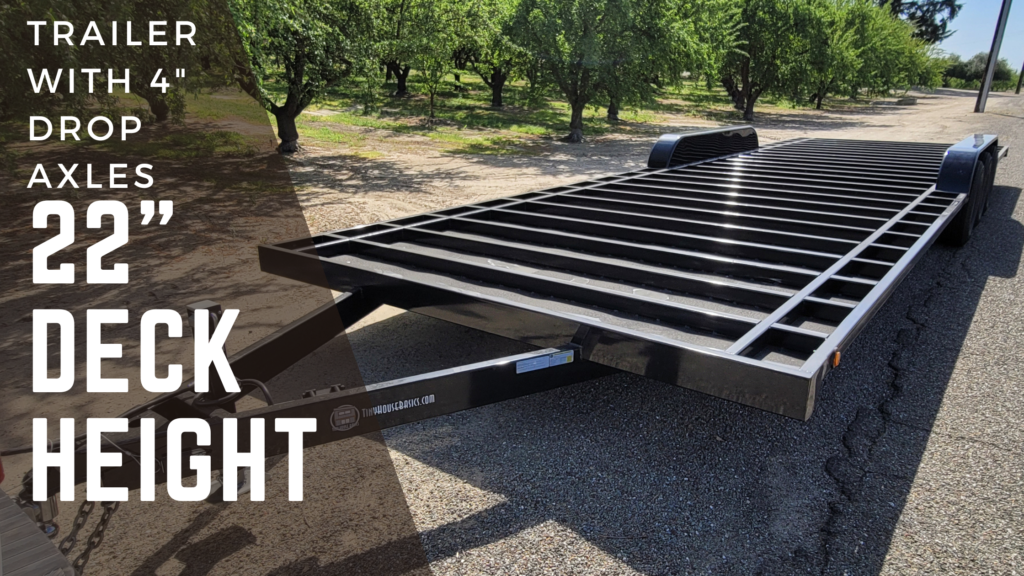

If you want to modify a New Zealand Tiny House Design to work with a drop axle trailer, you may have to be creative with your layout. In the design below, we converted the central doorway commonly found in NZ tiny houses into a window. We moved the entry doorway to the kitchen and added an auxiliary doorway at the rear of the tiny house.

Additional Information for Tiny Houses in the United States:
In the US, regulations do vary by state, The typical maximum width for a trailer is 8ft 6in (2.59m), but in some states, like Hawaii, the standard width can be 9ft without permits. These regulations safeguard all road users and allow for easy transport of tiny houses across states without breaking local laws.
However, it’s worth noting that in the US, there’s a growing trend of building larger tiny houses, especially for those who are looking to live in them full-time. These larger designs challenge the traditional “tiny” concept, providing more amenities and space. They cater to families or those less inclined to downsize significantly, ensuring long-term practicality in tiny living. When choosing a larger size tiny house, we always recommend utilizing one of our recommended professional shippers to handle the trailer transport and if you need moving of the tiny house when it’s complete. If we could have done it all over again, we would have built a 10′ wide tiny house if we had known better back in 2014.
Tiny House Designs & Materials for Weight Efficiency:
Framing Materials
Due to the maximum limit of 7,716lbs for a Tiny House In New Zealand, Many opt to pay the higher cost for steel framing to save weight. Framing members in NZ are only 2×3 while in the United States, The standard wood framing is 2×4 lumber. Wood framing is the most popular choice in the US due to ease of use, ease of modification, and change and it also doesn’t skyrocket the cost of the rest of your tiny house build. Metal studs will require specialized electrical and plumbing components and a large increase in labor throughout the rest of the build. For example, when installing your interior walls on metal studs, you must screw the paneling (shiplap or Tongue & groove) to the studs, fill in each screw with filler, and sand down before you paint. With wood framing, you can use nails.
Interior Walls
In New Zealand, marine and lightweight plywood serve as interior wall linings to minimize weight building materials like drywall can add significant weight to a tiny house, so lightweight alternatives are essential. This also applies in the United States. People commonly use 1/2in Sanded Plywood or Shiplap/tongue and groove materials.
Smaller Designs
To maintain the weight limit, many opt for smaller designs. Compared to the US and Canada, most tiny homes in NZ are often 1/2 the size in length only. This is a reflection of the strict weight limits and the desire to remain mobile. Keep in mind New Zealand Tiny Houses are Still 1ft 1in taller than the Average United States Tiny House. When a NZ Tiny House Design impresses you with its loft height, remember they have the advantage of building their tiny houses 13in taller than ours!
Fewer Heavy Objects
Tiny homes in NZ often have fewer and smaller windows and doors. Builders often construct cabinets from lightweight materials and sometimes install them on-site after transport. This approach ensures that the tiny house remains within the weight limits during transport. Aluminum windows are also more common in NZ, while in the US we use vinyl, Aluminum, and Fiberglass for window materials. People typically use aluminum in marine environments.
Flooring
Vinyl, laminate, or parquet flooring are common choices over solid timber floors. Though timber floors provide a cozy, natural aesthetic, their weight can be a concern, leading to their limited use in NZ compared to the US. In the US, popular flooring choices include Laminate, “Luxury” vinyl, Engineered flooring, and solid wood. Keep in mind, if you use Engineered or Solid you will be adding a lot more insulation to your home so that will save on energy usage no matter the season.
Tile
In New Zealand Tiny House Designs, people prefer faux tiles, such as Duma wall, for their lightweight properties. They offer the look and feel of traditional tiles without the added weight. In the United States, people favor real tiles, be it ceramic, glass, or clay. In the United States, people favor real tiles made of ceramic, glass, or clay. However, they typically limit tiled areas to bathrooms and kitchen backsplashes to reduce overall weight.
Siding
In New Zealand, people choose metal cladding over timber for its weight efficiency in siding/cladding. It offers a modern look and can be more resistant to the elements compared to traditional timber. In the U.S. We favor diverse options such as T1-11, Cedar, Metal Standing Seam, and Knotwood. Without the weight constraints like in NZ, we enjoy greater flexibility.
Shear Walls
Interestingly enough, in New Zealand, Builders don’t use a shear wall under their siding, they fasten the exterior siding directly to the framing and the only thing underneath is a simple building wrap. For more information on what a shear wall is, see this article in Fine Homebuilding: How it works, Shear Walls
Conclusion:
The tiny house movement, while global, has regional nuances that reflect the local regulations, climate, culture, Building Practices, and materials available for individual tiny house designs. What you have to work with in space can affect everything. Let’s see what you can do in the US when modifying from a NZ tiny house designs. Here is the simplest breakdown of differences in interior space:
- New Zealand: Trailer Deck Height 18in Above Grade, Max Height 14ft 7in. Roof Thickness 5in. Available interior height for both levels: 12ft 8in.
- United States: Trailer Deck Height 22in Above Grade with drop axles, Max Height 13ft 6in. Roof Thickness 7in. Available interior height for both levels: 11ft 1in.
New Zealand Tiny Houses Have 1ft 7in of Extra Interior Height than United States Tiny Houses!
While the US offers a bit more flexibility in terms of size and materials, New Zealand’s regulations have led to some innovative solutions and designs also. Regardless of the location, the core principle remains the same: living simply and sustainably. As the movement continues to grow, it will be interesting to see how different countries adapt and evolve their regulations to accommodate this new way of living.
United State Resources/References:
New Zealand Resources/References:
https://www.tinyeasy.co.nz/gotiny-blog/how-to-design-a-tiny-home-in-nz-important-things-to-consider
https://www.qldc.govt.nz/media/gxypqriq/qldc_tiny-homes-factsheet_dec21.pdf
https://tinyhousehub.co.nz/howToGuides/tiny-houses-on-wheels-how-big-can-i-legally-build\
https://bayengineering.co.nz/trailers/bes-detachable-deck-tiny-house-trailers/



